- Openssl Generate Aes Key Without Passphrase
- Aes Key Aade
- Openssl Generate Aes Key From Passphrase
- Openssl Generate Aes Key Without Passphrase Software
Demo of AES encryption in both ECB and CBC mode using OpenSSL toolkit. How to generate an OpenSSL CA. Those who want to start creating certificates right away without reading this whole document should skip to the summary. Create key¶ The Cookbook recommends putting passphrases on key files, but says it doesn’t really worsen security on a production web server to put the passphrase in a file next to the key file — if an attacker is on the system, they can probably extract the decrypted key from the web server memory anyway. OpenSSL is an open-source implementation of the SSL protocol. There is a lot of OpenSSL commands which you could use for various operations.
SSH login to Linux server
SSH login with provide more security to the server. It provides extra layer of security for the server. It uses public – private key authentication with server which prevents anyone login to the server with out private key. That means login with simple username and password can be depreciated and new two level of security can be added.
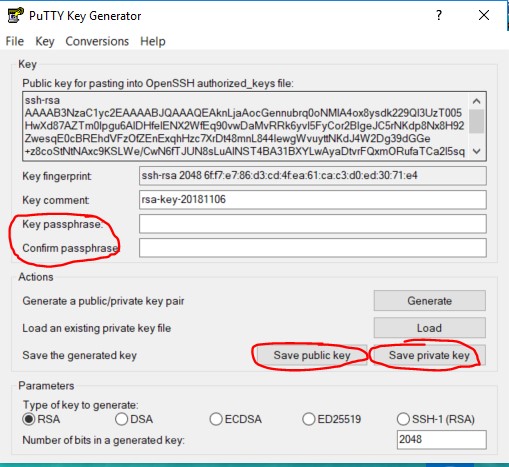
Generate public / private key:
We can generate keys by different ways. For better understanding please click here.
Create SSH login for User.
Enable SSH only login:
If we need to set SSH login to particular users only then, set that user name in Allowusers parameter.
Some of this from http://www.coresecuritypatterns.com/blogs/?p=763,http://www.bogpeople.com/networking/openssl.shtml,and (most recently) fromhttps://www.feistyduck.com/library/openssl-cookbook/,which was at the 3rd edition (Feb 2021) when I downloaded it.
End-user Functions¶
Create key¶
The Cookbook recommends putting passphrases on key files, but says itdoesn’t really worsen security on a production web server to put thepassphrase in a file next to the key file — if an attacker ison the system, they can probably extract the decrypted key from theweb server memory anyway. The point of the passphrase is to protectthe key file when it’s not deployed to your production server.
Create a 2048-bit key pair:
The key file is text, but inscrutable. You can see what’s actuallythere using:
The “key” is actually a private/public key pair.You can extract just the public part:
Create a password-protected 2048-bit key pair:
OpenSSL will prompt for the password to use. Algorithms: AES (aes128, aes192 aes256), DES/3DES (des, des3).
Remove passphrase from a key:
Extract public key:
Getting Certificates¶
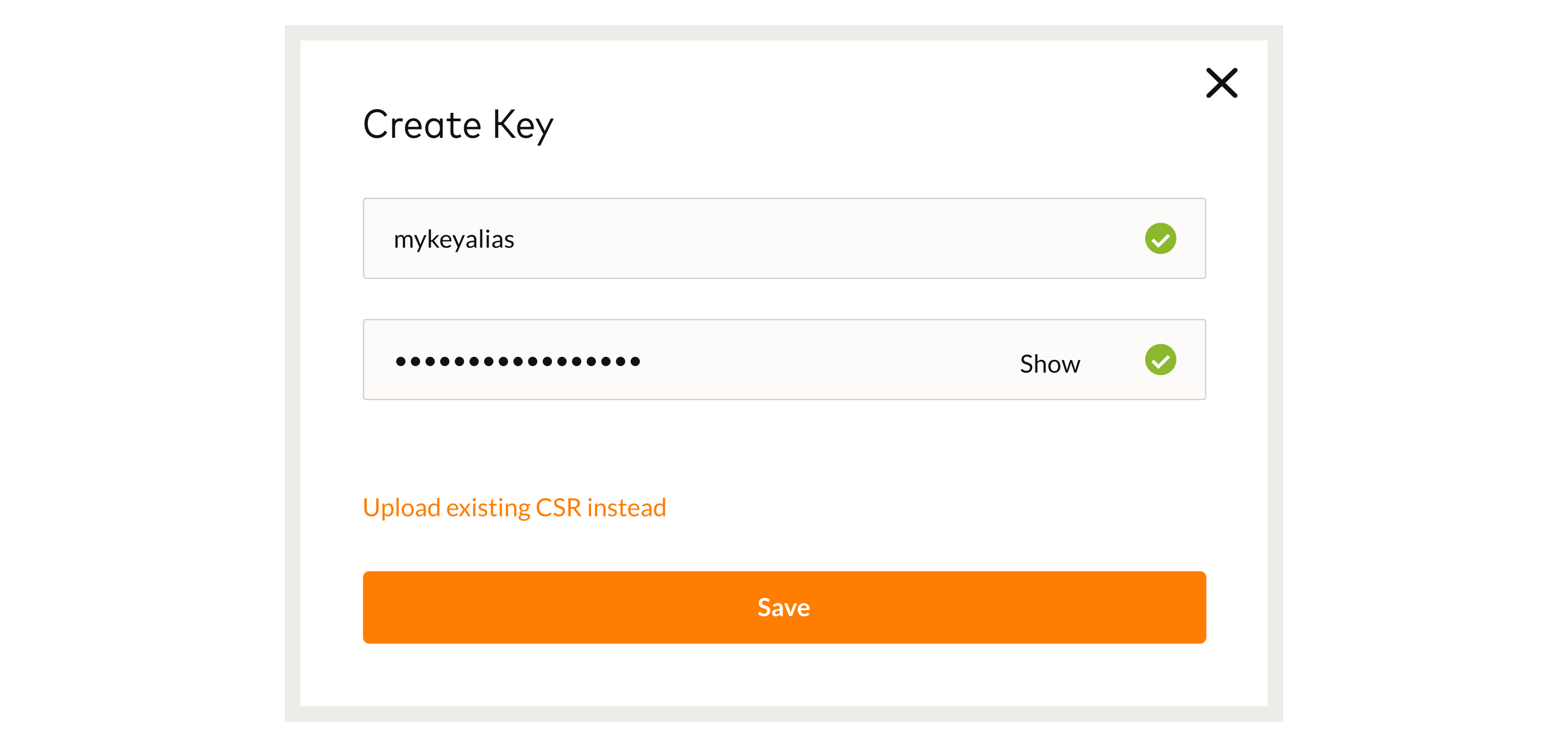
Create Certificate Request and Unsigned Key:
More thorough example:
Create a self-signed certificate:
-x509 identifies it as a self-signed certificate and -set_serial sets the serial number for the server certificate.
Create a single file that contains both private key and the self-signed certificate:
Fingerprint for Unsigned Certificate:
Display Certificate Information:
Creating a PEM File for Servers:
Download some server’s certificate:
(then hit ^C out of the interactive shell)
Viewing Certificate Contents¶
X.509 certificates are usually stored in one of two formats. Most applicationsunderstand one or the other, some understand both:
DER which is raw binary data.
PEM which is a text-encoded format based on the Privacy-Enhanced Mail standard (see RFC1421). PEM-format certificates look something like this:
The command to view an X.509 certificate in DER format is:
Specify -informpem if you want to look at a PEM-format certificate.
Convert Between Formats¶
If you have a PEM-format certificate which you want to convert into DER-format, you can use the command:
PKCS12 files¶
PKCS12 files are a standard way of storing multiple keys and certificatesin a single file. Think of it like a zip file for keys & certificates,which includes options to password protect etc.
Don’t worry about this unless you need it because some application requiresa PKCS12 file or you’re given one that you need to get stuff out of.
Viewing PKCS12 Keystore Contents:
If you have two separate files containing your certificate and private key, both in PEM format, you can combine these into a single PKCS12 file using the command:
Encrypting and signing things¶
Signing E-mails:
Sign some text:
Verify signature:
Encrypt and decrypt a single file:
Simple file encryption:
(password will be prompted)
Simple file decryption:
tar and encrypt a whole directory:

tar zip and encrypt a whole directory:
Certificate Authority Functions¶
When setting up a new CA on a system, make sure index.txt and serial exist (empty and set to 01, respectively), and create directories private and newcert.
Edit openssl.cnf - change default_days, certificate and private_key, possibly key size (1024, 1280, 1536, 2048) to whatever is desired.
Openssl Generate Aes Key Without Passphrase
Create CA Certificate:
Export CA Certificate in DER Format:
Revoke Certificate:
Generate Certificate Revokation List:
Aes Key Aade
Sign Certificate Request:
Create Diffie-Hoffman Parameters for Current CA:
Openssl Generate Aes Key From Passphrase
Creating Self-Signed Certificate from Generated Key:
Openssl Generate Aes Key Without Passphrase Software
Use only when you’ve no CA and will only be generating one key/certificate (useless for anything that requires signed certificates on both ends)